
The Connection of Fitness and Mental Health from Childhood Through Adolescence

A recent Finnish study has shed light on an intriguing connection between physical fitness and mental health during childhood and adolescence. As mental health issues increasingly challenge young people, with estimates suggesting that 25% to 30% of them face significant struggles, these findings underscore the importance of fostering physical fitness early in life. Emphasizing fitness during formative years could serve as a preventive measure against potential mental health problems down the line.
The Study’s Findings
Conducted by the Faculty of Sport and Health Sciences at the University of Jyväskylä and the Institute of Biomedicine at the University of Eastern Finland, this study monitored the physical fitness levels of 241 adolescents over an eight-year period. Participants’ cardiorespiratory fitness and motor fitness were evaluated from childhood into adolescence, revealing some compelling insights.
Cardiorespiratory Fitness

Freepik | Teens who got better at running, cycling, and other heart-pumping activities felt less stressed and depressed.
Improvements in cardiorespiratory fitness were notably associated with reduced stress and depressive symptoms during adolescence. This aspect of fitness, often linked to activities such as running and cycling, plays a crucial role in overall health.
Motor Fitness
While also beneficial, motor fitness, which includes skills like coordination and agility, showed a weaker correlation with depressive symptoms compared to cardiorespiratory fitness. However, it still contributed to better cognitive function and less stress during adolescence.
Screen Time’s Impact
An interesting element of the study was the role of screen time in understanding the relationships between fitness and mental health. Adolescents who engaged in higher screen time tended to experience more mental health challenges, partially explaining the associations observed. This highlights the need for balance in physical activities and screen usage.
The Need for Investment in Physical Fitness
These findings advocate for proactive strategies aimed at enhancing physical fitness among children and adolescents. A societal effort is essential, suggesting that communities, schools, and families must collectively promote physical activities. Increasing participation in sports, exercise, and leisure activities can pave the way for healthier generations.
“Community support is vital in developing physical fitness in children and adolescents. It’s important to encourage active participation in various activities, whether during school hours, in free time, or through hobbies,” explains a researcher involved in the study. This collaborative approach emphasizes the shared responsibility in nurturing future well-being.
Longitudinal Insights
The research stems from the ongoing Physical Activity and Nutrition in Children (PANIC) study, which is dedicated to understanding the links between physical activity, nutrition, and health outcomes. The PANIC study focuses on addressing major cardiometabolic diseases, utilizing longitudinal data to reveal insights that could lead to early diagnosis and preventive strategies. By understanding how fitness relates to mental health, a more comprehensive picture of adolescent well-being emerges.
Benefits Beyond Physical Health
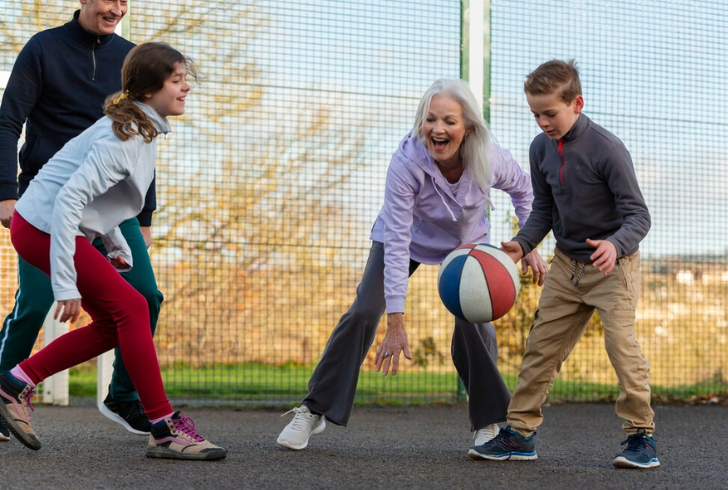
Freepik | Regular physical activity can help kids and teens manage stress and anxiety.
The connection between fitness and mental health extends beyond mere statistics; it signifies a holistic approach to well-being. Regular physical activity not only strengthens the body but also enhances emotional resilience, cognitive function, and overall quality of life. When children are encouraged to stay active, they develop habits that benefit them throughout their lives.
1. Enhanced Mood – Exercise releases endorphins, often referred to as “feel-good” hormones. Regular participation in physical activities can elevate mood and foster a more positive outlook on life.
2. Social Skills – Engaging in group sports or activities helps children develop teamwork and communication skills, contributing to better social interactions and friendships.
3. Stress Management – Physical fitness provides effective coping mechanisms for stress. Children and adolescents who participate in regular physical activities often report lower levels of anxiety and stress.
A Step Towards Better Mental Health
The relationship between fitness and mental health highlights the necessity of prioritizing physical activity from a young age. By investing in the physical fitness of children and adolescents, society can work towards alleviating mental health issues, fostering resilience, and promoting a healthier future.
Encouraging active lifestyles and creating supportive environments will yield positive outcomes not only for individuals but also for communities at large. The path to better mental health begins with the foundation of fitness established early in life.
By emphasizing fitness as a fundamental aspect of well-being, a brighter, healthier future for the youth can be achieved.
More in Health & Fitness
-
`
Mahershala Ali and Amatus-Sami Karim’s Decade-Long Marriage
Who is Mahershala Ali married to? This question often arises when discussing the acclaimed actor. Mahershala Ali, the talented and versatile...
August 5, 2024 -
`
Is It Normal to Be Sore After a Massage? 9 Ways to Relieve Soreness
Is it normal to be sore after a massage? Many people schedule a massage to drift into a state of relaxation...
August 3, 2024 -
`
Delicious Pescatarian Breakfast Ideas
Exploring new breakfast ideas can be a delightful way to start your day, especially when they align with a pescatarian diet....
July 24, 2024 -
`
Is Phuket Worth Visiting in 2024?
Phuket, Thailand’s gem of an island, has long attracted travelers with its pristine beaches, lively nightlife, and cultural treasures. The question...
July 19, 2024 -
`
What is the Best Way to Melt Chocolate for Any Recipe?
Chocolate is a beloved ingredient in many desserts, from ganache and cake batters to decadent drizzles over ice cream. Knowing what...
July 12, 2024 -
`
How to Plan a Backpacking Trip Like a Pro in 16 Steps
Planning a backpacking trip can be as thrilling as it is daunting, especially if you’re keen to make every moment count....
July 5, 2024 -
`
How to Build Fast-Twitch Muscles in 5 Simple Steps
Have you ever wondered how to build fast-twitch muscles? These powerful muscle fibers are key to explosive strength and speed. Whether...
June 20, 2024 -
`
How to Create the Perfect Goulash Recipe Every Time
As autumn leaves paint the landscape in warm hues, nothing complements the chill in the air quite like a bowl of...
June 15, 2024 -
`
Fun Things to Do When Bored With Friends
When boredom strikes, especially when you are with friends, it is easy to fall into the trap of mindlessly scrolling through...
June 4, 2024















You must be logged in to post a comment Login